When it comes to high school mathematics, Algebra 2 holds a special place. It’s the bridge between basic algebraic concepts and more advanced topics, preparing students for higher-level math courses. The Big Ideas Math Algebra 2 curriculum stands out for its innovative approach to teaching and learning algebra. Let’s dive into what makes this curriculum unique and explore some core concepts and strategies for mastering Algebra 2.
What Makes Big Ideas Math Algebra 2 Unique?
Big Ideas Math Algebra 2 is not just another textbook. It’s a comprehensive learning experience designed to engage students with interactive elements and technology. The curriculum emphasizes understanding over memorization, using a variety of teaching methods to cater to different learning styles. Whether through hands-on activities, digital resources, or real-world applications, Big Ideas Math makes algebra both accessible and enjoyable.
Core Concepts in Big Ideas Math Algebra 2
Algebra 2 is packed with essential topics that build on Algebra 1 and prepare students for calculus and other advanced math courses. Some of the key concepts include:
- Functions and their properties
- Polynomial expressions and equations
- Rational expressions and equations
- Exponential and logarithmic functions
Detailed Exploration of Functions
Functions are at the heart of Algebra 2. Here’s a closer look at the different types of functions you’ll encounter:
Understanding Linear Functions
Linear functions are the foundation of algebraic understanding. They are represented by equations of the form \(y=mx+b\) where \(m\) is the slope and \(b\) is the y-intercept. These functions describe a straight line on a graph and are crucial for understanding more complex functions.
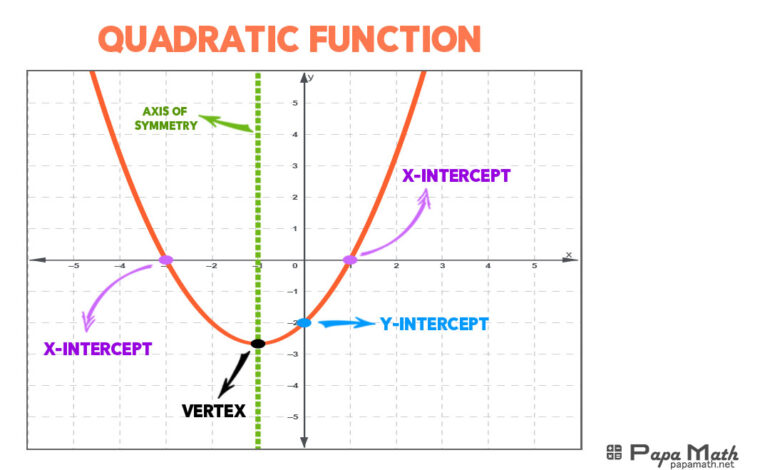
Exploring Quadratic Functions
Quadratic functions introduce students to parabolas. These functions are represented by \(y=ax^{2}+bx+c\). Understanding how to graph these functions, find their vertices, and solve quadratic equations using methods like factoring and the quadratic formula is essential.
Analyzing Higher-Degree Polynomial Functions
As students progress, they encounter higher-degree polynomials. These functions, which include cubic and quartic equations, have more complex graphs and solutions. Understanding the behavior of these functions and their roots is a significant part of Algebra 2.
Polynomial Expressions and Equations
Basics of Polynomials
Polynomials are expressions that involve sums of powers of variables. For example,
$$2x^{3}-2x^{2}+x-5$$
Is a polynomial. Learning to add, subtract, and multiply polynomials is a key skill.
Solving Polynomial Equations
Solving polynomial equations often involves factoring or using the Rational Root Theorem. These techniques help in finding the solutions or roots of the equations, which are the values of \(x\) that make the equation zero.
Real-World Applications of Polynomials
Polynomials are not just abstract concepts; they have real-world applications. For example, they can model the trajectory of a ball, population growth, or economic trends.
Rational Expressions and Equations
Simplifying Rational Expressions
Rational expressions are fractions that contain polynomials in the numerator and denominator. Simplifying these expressions involves finding common factors and reducing them to their simplest form.
Solving Rational Equations
Solving rational equations requires finding a common denominator, eliminating the fractions, and then solving the resulting polynomial equation. It’s important to check for extraneous solutions that may arise.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Students often make mistakes when dealing with rational expressions, such as forgetting to factor completely or not checking for excluded values. Being aware of these pitfalls can help avoid them.
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
Understanding Exponential Growth and Decay
Exponential functions describe situations where quantities grow or decay at a constant rate. These functions have the form \(y=ab^{x}\), where \(𝑎\) is the initial amount and \(b\)is the growth factor. They are used in fields like biology, finance, and physics.
Logarithmic Functions and Their Applications
Logarithms are the inverse of exponential functions. They help solve equations involving exponentials and have applications in areas such as measuring sound intensity (decibels) and the pH scale in chemistry.
Real-Life Applications
Exponential and logarithmic functions are used in various real-life scenarios, such as calculating compound interest, population growth models, and radioactive decay.
Using Big Ideas Math Algebra 2 for SAT and ACT Preparation
Algebra 2 concepts are heavily tested on standardized tests like the SAT and ACT. Big Ideas Math Algebra 2 provides comprehensive coverage of these topics, making it an excellent resource for test preparation.
Key Concepts Covered in Standardized Tests
Understanding functions, polynomials, and exponential equations is crucial for doing well on these tests. Big Ideas Math ensures students have a strong grasp of these concepts.
Tips for Effective Study Using Big Ideas Math
Regular practice, utilizing the interactive elements, and reviewing detailed solutions are effective ways to prepare for standardized tests using Big Ideas Math.
Resources for Big Ideas Math Algebra 2 Answers
Finding reliable answers to homework problems is crucial for understanding the material.
Where to Find Reliable Answers
The Big Ideas Math website, teacher resources, and study guides are great places to find accurate answers.
Importance of Understanding Solutions Rather Than Memorizing
It’s important to understand the steps and logic behind each solution instead of just memorizing answers. This approach ensures a deeper comprehension and ability to tackle similar problems in the future.
Comparing Big Ideas Math Algebra 2 with Other Curricula
Big Ideas Math vs. Saxon Math Algebra 1
Saxon Math focuses on incremental learning and frequent review, while Big Ideas Math emphasizes understanding and interactive learning. Both have their strengths, depending on the student’s learning style.
Big Ideas Math vs. Math U See Algebra 1
Math U See is known for its visual and hands-on approach, making it great for visual learners. Big Ideas Math, on the other hand, integrates technology and real-world applications, providing a comprehensive understanding of algebraic concepts.
Practical Examples and Problem-Solving Strategies
Step-by-Step Solutions to Sample Problems
Here’s a step-by-step solution to a common Algebra 2 problem:
Example: Solve the quadratic equation \(2x^{2}-4x-6=0\) using the quadratic formula.
First Identify the values of \(a,b\) and \(c\) by compare the equation \(ax^{2}+bx+c=0\) it follows that:
$$a=2,b=-4,c=-6$$
The quadratic formula is:
$$x=\frac{-b\pm \sqrt{b^{2}-4ac}}{2a}$$
Substitute the values into the above formula;
$$x=\frac{-(-4)\pm \sqrt{-4^{2}-4(2)(-6)}}{2(2)}$$
Solve the equation for \(x\) it follows that:
$$x=\frac{4\pm 8}{4}$$
Solve the equation for \(x\) it follows that:
$$x=3,x=-1$$
Strategies for Tackling Difficult Questions
Breaking down problems into smaller steps, checking your work, and using online resources for additional practice can make challenging questions more manageable.
Interactive and Online Resources for Big Ideas Math Algebra 2
Online Platforms and Tools
The Big Ideas Math website offers a range of online tools, including interactive quizzes, videos, and practice problems that help reinforce learning.
Benefits of Interactive Learning
Interactive learning keeps students engaged and allows for immediate feedback, making it easier to grasp complex concepts.
Common Challenges Students Face in Algebra 2
Typical Difficulties and How to Overcome Them
Students often struggle with abstract concepts and multi-step problems. Practice, patience, and asking for help when needed are key to overcoming these challenges.
Tips for Staying Motivated and Engaged
Setting small goals, rewarding progress, and relating math to real-life situations can help maintain motivation and interest.
The Role of Teachers and Parents in Supporting Students
Encouraging a Growth Mindset
Teachers and parents can help by fostering a growth mindset, emphasizing effort and learning from mistakes rather than just focusing on grades.
Providing Additional Resources and Support
Offering extra practice materials, tutoring, and positive reinforcement can make a big difference in a student’s success.
For a comprehensive overview, read our article on “Define Algebra and Branches of Algebra“
FAQs
What are the main topics covered in Big Ideas Math Algebra 2?
The main topics include functions, polynomial expressions, rational expressions, and exponential and logarithmic functions.
How can I find the answers to Big Ideas Math Algebra 2 problems?
Reliable answers can be found on the Big Ideas Math website, teacher resources, and study guides.
What are some effective study strategies for Algebra 2?
Regular practice, using interactive tools, and reviewing detailed solutions are effective strategies.
How does Big Ideas Math Algebra 2 compare to other math curricula?
Big Ideas Math emphasizes understanding and interactive learning, while other curricula like Saxon Math focus on incremental learning and frequent review.
What resources are available for additional practice and learning?
Online platforms, interactive quizzes, videos, and practice problems on the Big Ideas Math website provide excellent additional resources.
For more in-depth solutions and explanations, refer to “Big Ideas Math Algebra 2.”
Conclusion
Algebra 2 is a critical step in a student’s math journey, and the Big Ideas Math Algebra 2 curriculum offers a unique, interactive, and effective way to master this subject. By understanding core concepts, utilizing available resources, and practicing regularly, students can achieve a solid understanding and excel in Algebra 2.
“Please feel free to ask your query, and I’ll be happy to answer your query.“